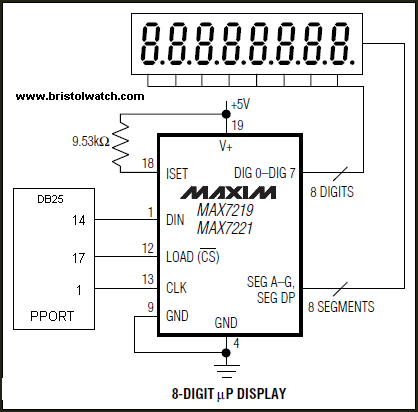
Python PC Printer Port MAX7219 LED Display Serial ADC Interface
This program shows how to connect a MAX7219 8-digit LED display to the IBM PC printer port. This program converts an integer to binary coded decimal (BCD) the displays the count on the right four digits of the 8-digit, 7-segment LED display.
Here we read the serial data from a TLC548 analog to digital converter.
The program is written in Python and runs under Linux. To use this one must setup a module pyparallel. How to set this up is on my webpage Programming the PC Printer Port in Python
Here I've used generic MAX7219 modules from Ebay and wire them as shown above.
View DB25 Printer port connector.
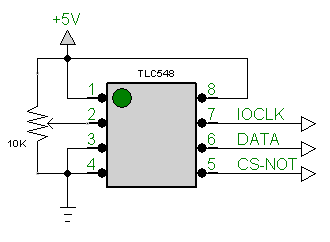
Connect the ADC as follows:
# Connect to TLC548 CS-NOT pin 5 to Db25 pin 3 D1
# Connect to TLC548 CLK pin 7 to Db25 pin 2 D0
# Connect TLC548 Pin 6 DATA OUT to Db25 pin 15
The program is written in Python and runs under Linux. To use this one must setup a module pyparallel. How to set this up is on my webpage Programming the PC Printer Port in Python
#!/usr/bin/env python
# File pportlcdADC.py
# http://www.bristolwatch.com/pport/index.htm
# By Lewis Loflin - lewis@bvu.net
# Must use my version of pyparallel on website for p.data().
# This combines two earlier modules
# pport7219.py and pporttlc548bits.py
# Programs reads value from ADC and
# displays 8-digit LED display.
import parallel
import time
p = parallel.Parallel()
# init i/o pins
p.setDataStrobe(0) # Pin 1 use as CLK on MAX7219 LOW to HIGH to LOW
p.setAutoFeed(0) # Pin 14 use as data bit
p.getInError() # Pin 15 Input NC
p.setInitOut(1) # pin 16 NC
p.setSelect(0) # pin 17 CS connect to
# LD pin on MAX7219 LOW to HIGH to LOW
# clock bit into MAX7219
def pulseCLK():
p.setDataStrobe(1)
# time.sleep(.01)
p.setDataStrobe(0)
return
# clock data-location into MAX7219
def pulseCS():
p.setSelect(1)
# time.sleep(.01)
p.setSelect(0)
return
# shift byte into MAX7219
# MSB out first!
def ssrOut(value):
for x in range(0,8):
temp = value & 0x80
if temp == 0x80:
p.setAutoFeed(1) # set data bit HIGH
else:
p.setAutoFeed(0)
pulseCLK()
value = value << 0x01 # shift left
time.sleep(.001)
p.setDataStrobe(0)
p.setAutoFeed(0)
return
# convert an 8-bit number to a binary string
def convBinary(value):
binaryValue = 'b'
for x in range(0,8):
temp = value & 0x80
if temp == 0x80:
binaryValue = binaryValue + '1'
else:
binaryValue = binaryValue + '0'
value = value << 1
return binaryValue
# initialize MAX7219 8 digits BCD
def initMAX7219():
# set decode mode
ssrOut(0x09) # address
# ssrOut(0x00); // no decode
ssrOut(0xFF) # 4-bit BCD decode eight digits
pulseCS();
# set intensity
ssrOut(0x0A) # address
ssrOut(0x0D) # 5/32s
pulseCS()
# set scan limit 0-7
ssrOut(0x0B); # address
# ssrOut(0x07) # 8 digits
ssrOut(0x03) # 4 digits
pulseCS()
# set for normal operation
ssrOut(0x0C) # address
# ssrOut(0x00); // Off
ssrOut(0x01) # On
pulseCS()
for x in range(0,9):
ssrOut(x)
ssrOut(0)
pulseCS()
return
def writeMAX7219(data, location):
ssrOut(location)
ssrOut(data)
pulseCS()
return
'''
; Pins on the TLC548 8-bit ADC:
; 1 -> Ref + -> connect to Vcc
; 2 -> analog in
; 3 -> Ref - -> connect to GND
; 4 -> GND
; 5 -> CS-NOT -> chip select active LOW
; 6 -> DATA OUT
; 7 -> CLK
; 8 -> Vcc
'''
# see pporttlc548bits.py
# Connect to TLC548 CLK pin 7 to DB25 pin 2
def writeD0(bit_val):
if bit_val == 1:
p.setData(p.data() | 1) # set bit 0
else: # clear bit 0
p.setData(p.data() & (255 - 1))
return
writeD0(0) # set TLC548 CLK pin 7 LOW
# Connect to TLC548 CS-NOT pin 5 to DB25 pin 3
def writeD1(bit_val):
if bit_val == 1:
p.setData(p.data() | 2) #set bit 1
else: # clear bit 1
p.setData(p.data() & (255 - 2))
return
writeD1(1) # set TLC548 CS-NOT pin 5 HIGH
# data LSB first
# enable TLC548 CS-NOT LOW
# set CLK HIGH
# read data bit shift left
# set CLK LOW
def readADC():
temp = 0
writeD1(0) # enable CS-NOT LOW
# time.sleep(.01)
for i in range(0,7): # loop here 7 times
writeD0(1) # CLK HIGH
temp = temp + p.getInError() # get bit
temp = temp << 1 # shift 1 bit left
writeD0(0) # CLK LOW
writeD0(1) # CLK HIGH
temp = temp + p.getInError() # get bit 8
writeD0(0) # CLK LOW
writeD1(1) # CS-NOT HIGH
return temp
initMAX7219() # setup MAX7419
while 1:
j = readADC()
# get 1st digit j
digit = j % 10
writeMAX7219(digit, 1)
j = j / 10
digit = j % 10
writeMAX7219(digit, 2)
j = j / 10
digit = j % 10
writeMAX7219(digit, 3)
j = j / 10
digit = j % 10
writeMAX7219(digit, 4)
j = j / 10
time.sleep(.2)
exit
Download pport-1.0.iso from Sourceforge.com then burn to DVD (file size 920 meg.), insert into DVD drive and reboot. Make sure PC is set to boot from DVD ROM.
This is pre-configured by myself to use Python to control the printer port. Python can be run from IDLE or Geany.
All of my PPORT electronics projects will work without installation to a PC.
Programs can be saved to thumb drive in LIVE mode.
Projects
Below are listed a series of projects using pyparallel and electronics. Starting with routines I wrote to aid students I'd advise walking through this in sequence. Have fun and send comments and/or corrections to lewis@bvu.net.
- Introduction to Python Bitwise Operations
- Python Bitwise Operations by Example
- Using the PC Printer Port series:
- Programming the PC Printer Port in Python
- Additional Commands for Py-Parallel
- Controlling Data Bits on the PC Parallel Port
- Connecting Switches to the PC Printer Port with Python
- Reading an Analog Voltage Through the PC Printer Port Part 1
- Reading an Analog Voltage Through the PC Printer Port Part 2
- Controlling a Serial LCD Display on a PC Printer Port with Python
- Serial ADC and LCD Display with PC Printer Port with Python
- Controlling MAX7219 LED Display with PC Printer Port with Python
- MAX7219 8-Digit LED Display and Serial ADC in Python
- Project pages:
- Part 1: Read Arduino with PC Printer Port
- Part 2: Better way to Read Arduino Through the PC Printer Port
- Part 3: Read-Write an Arduino Through a PC Printer Port
- Part 4: Control LCD Display and Arduino from the PC Printer Port
- Arduino sketches needed by programs:
- pportArduino1.ino read only after reset.
- pportArduino2.ino reset once and multiple reads.
- pportArduino3.ino reset once read write Arduino infinite times - multiple commands.
- Related Raspberry Pi projects:
- Connect Serial LCD to Raspberry Pi
- Serial Read from Arduino to Raspberry Pi
- Arduino Raspberry Pi Interface with LCD Display
Linux Videos
- Live Linux Distro for Using Printer Port with Electronics
- Using the powerful Rox-Filer system in Linux
- Use FEH under Linux for a Wallpaper Setter
- How to create Symbolic links in Linux
- Printer Port Interfacing Videos:
- Connect Electronics to PC printer Port with Python
- Setup PC Printer Port with Python-Linux
- Use PC Printer Port to Read Analog Voltage
- Read-Write Arduino ADC PWN with Printer Port
- Printer Port to Serial LCD Display
- Connect Arduino to PC Printer Port for advanced control
Printer Port in C
- Exploring Digital Computer Electronics
- Hardware Review Connecting PC Parallel Ports
- Operation TB6600 Stepper Controller with PC Parallel Port
- Build or Buy Parallel Port Breakout Board?
- Build Serial HD44780 LCD Display Connect to Parallel Port
- Motherboards
- Presario 1999 CM1001 Gaming Computer Salvage
- Live Test 2002 VIA EPIA-800 Mini ITX Motherboard
- Salvage, Test 2012 AAEON EMB-B75A Industrial Motherboard
- Web Master
- Gen. Electronics
- YouTube Channel
- Arduino Projects
- Raspberry Pi & Linux
- PIC18F2550 in C
- PIC16F628A Assembly
- PICAXE Projects
Web site Copyright Lewis Loflin, All rights reserved.
If using this material on another site, please provide a link back to my site.